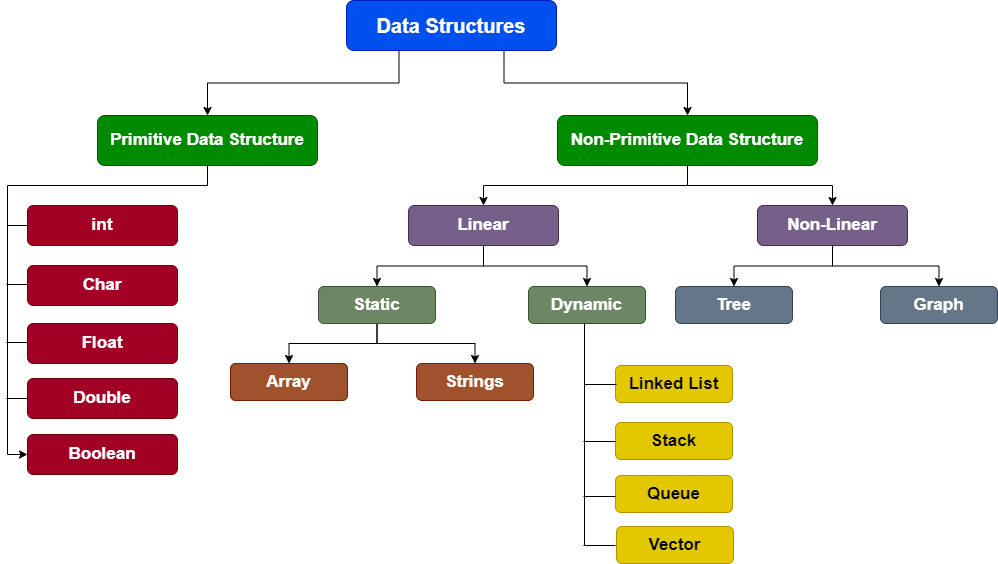
Data Structures – The logical or mathematical
model of a
particular organization of data is called Data Structures.
Data Types vs Data Structures
–
| Data Types | Data Structures |
|---|---|
| Data Type is the kind or form of a variable which is being used throughout the program. It defines that the particular variable will assign the values of the given data type only. | Data Structure is the collection of different kinds of data. That entire data can be represented using an object and can be used throughout the entire program. |
| Implementation through Data Types is a form of abstract implementation. | Implementation through Data Structures is called concrete implementation. |
| Can hold values and not data, so it is data less. | Can hold different kind and types of data within one single object. |
| Values can directly be assigned to the data type variables. | The data is assigned to the data structure object using some set of algorithms and operations like push, pop and so on. |
| No problem of time complexity. | Time complexity comes into play when working with data structures. |
| Examples: int, float, double etc. | Examples: stacks, queues, tree etc. |
Types of Data Structure
–
- Primitive
- Non-Primitive
Primitive Data Structure
– Those basic data structures which are pre-defined in standard library. It can store the
value of
only one
data type. It cannot contain null values. ie – int, char, float etc.
Non-Primitive Data Structure
– Those data structures which are user-defined (except strings) which can be easily
created
or
modified by
user. They can store multiple values and invoke methods to perform certain operations. ie –
string,
array
etc.
Linear Data Structure
– In linear data structure data is organized in sequential order.
Types of linear Data Structure
–
- Static
- Dynamic
Static Data Structure
– A static data structure is an organization or collection of data in memory which have a
fixed
size,
that is, it can store a limited amount of elements or data in it. ie – array, string.
Dynamic Data Structure
– A dynamic data structure is an organization or collection of data in memory which do not
have a
fixed size, that is, its size can be modified during the operations performed on it and can store a
variable
amount of elements or data in it. ie – linked list, queue, stack etc.
Types of Dynamic Data Structure –
- Linked list
- Stack
- Queue
Non-linear Data Structure
– In non-linear data structure data is organized in random order.
Types of non-linear data structures
- Trees
- Graphs
- Heaps
- Tries
- Maps
- Dictionaries
Difference between linear and non-linear data structure
–
| Linear Data Structure | Non-Linear Data Structure |
|---|---|
| In a linear data structure, data elements are arranged in a linear order where each and every element is attached to its previous and next adjacent. | In a non-linear data structure, data elements are attached in hierarchically manner. |
| In linear data structure, single level is involved. | Whereas in non-linear data structure, multiple levels are involved. |
| Its implementation is easy in comparison to non- linear data structure. | While its implementation is complex in comparison to linear data structure. |
| In linear data structure, data elements can be traversed in a single run only. | While in non-linear data structure, data elements can’t be traversed in a single run only. |
| In a linear data structure, memory is not utilized in an efficient way. | While in a non-linear data structure, memory is utilized in an efficient way. |
| Applications of linear data structures are mainly in application software development. | Applications of non-linear data structures are in Artificial Intelligence and image processing. |
| ie – array, stack, queue, linked list, etc. | ie – trees, graphs, heaps, dictionaries, tries, maps etc. |
Arrays –
- Used for storing fixed number of items that need fast access time at any point during program execution.
- Storing list of data elements belonging to same data type.
- Auxiliary storage for other data structures.
- Storage of binary tree elements of fixed count.
- Storage of matrices.
- Arrangement of the leader-board of a game can be done simply through arrays to store the score and arrange them in descending order to clearly make out the rank of each player in the game.
- A simple question Paper is an array of numbered questions with each of them assigned some marks.
- 2D arrays, commonly known as, matrices, are used in image processing.
- It is also used in speech processing, in which each speech signal is an array.
- Your viewing screen is also a multidimensional array of pixels.
- Book titles in a Library Management Systems.
- Online ticket booking.
- Contacts on a cell phone.
- For CPU scheduling in computer.
- To store the possible moves of chess on a chessboard.
- To store images of a specific size on an android or laptop.
Strings –
- Spam email detection.
- Plagiarism detection.
- Search engine.
- Digital forensic and information retrieval system.
- Spell checkers.
- In the database to check valid information of the user.
Linked list –
- Implementing stacks, queues, binary trees and graphs of predefined size.
- Implement dynamic memory management functions of the operating system.
- Polynomial implementation for mathematical operations
- Circular linked list is used to implement OS or application functions that require round robin execution of task
- Images are linked with each other. So, image viewer software uses a linked list to view the previous and the next images using the previous and next buttons.
- Web pages can be accessed using the previous and the next URL links which are linked using a linked list.
- The music players also use the same technique to switch between music.
- To keep the track of turns in a multiplayer game, a circular linked list is used.
- MS-Paint drawings and shapes are connected via a linked list on canvas.
- Escalators — Circular linked List.
- Each of the lines of code in an IDE internally is a record on a doubly-linked list.
- Left/Right swipe on Tinder uses a doubly-linked list.
- Social media content “feeds”.
- Used for symbol table management in a designing compiler.
- Used in switching between applications and programs (Alt + Tab) in the Operating system (implemented using Circular Linked List).
- Train coaches are connected to one another in a doubly-linked list fashion.
- It can be used to implement Stacks, Queues, Graphs, and Trees.
- To perform an undo operation.
- Back button.[LIFO]
- Syntax in the coding editor.
Stack –
- Temporary storage structure for recursive operations.
- Auxiliary storage structure for nested operations, function calls, deferred/postponed functions.
- Manage function calls.
- Evaluation of arithmetic expressions in various programming languages.
- Conversion of infix expressions into postfix expressions (polish notation).
- Checking syntax of expressions in a programming environment.
- Matching of parentheses.
- String reversal.
- In all the problems solutions are based on backtracking.
- Used in depth first search in graph and tree traversal.
- Operating System function.s
- UNDO and REDO functions in an editor.
Queue –
- It is used in breadth search operations in graphs.
- Job scheduler operations of OS like a print buffer queue, keyboard buffer queue to store the keys pressed by users.
- Job scheduling, CPU scheduling, Disk Scheduling.
- Priority queues are used in file downloading operations in a browser.
- Data transfer between peripheral devices and CPU.
- Interrupts generated by the user applications for CPU.
- Calls handled by the customers in BPO.
Trees –
- Implementing the hierarchical structures in computer systems like directory and file system.
- Implementing the navigation structure of a website.
- Code generation like Huffman’s code.
- Decision making in gaming applications.
- Implementation of priority queues for priority based OS scheduling functions.
- Parsing of expressions and statements in programming language compilers.
- For storing data keys for DBMS for indexing.
- Spanning trees for routing decisions in computer and communications networks.
- Hash trees.
- path-finding algorithm to implement in AI, robotics and video games applications.
Graphs –
- Representing networks and routes in communication, transportation and travel applications.
- Routes in GPS.
- Interconnections in social networks and other network based applications.
- Mapping applications.
- Ecommerce applications to present user preferences.
- Utility networks to identify the problems posed to municipal or local corporations.
- Resource utilization and availability in an organization.
- Document link map of a website to display connectivity between pages through hyperlinks.
- Robotic motion and neural networks.
Matrix –
- In geology, matrices are used for making seismic surveys.
- Used for plotting graphs, and statistics and also to do scientific studies and research in almost different fields.
- Matrices are also used in representing real-world data like the population of people, infant mortality rate, etc.
- They are the best representation methods for plotting surveys.
- For refraction and reflection in science optics.
- Electronic circuits and quantum physics.
- Media player.
- Mailing list.
- Symbol table creation.